Principle
Proteins are first precipitated by trichloroacetic acid. The urea present in the protein-free filtrate reacts with diacetyl monoxime in a hot acidic medium in presence of ferric/cadmium ions and thiosemicarbazide to form pink or red colored complex- diazine. The intensity of the color developed is measured photometrically at 530nm, which is directly proportional to the concentration of the urea present in the fluid.
Requirements
- Apparatus:
Colorimeter
Conical flasks and test tubes to hold 20ml
Pipettes: 50ul, 0.1ml, 0.5ml, 5 ml
Measuring cylinder, 50 ml
Water bath at 100°C - Reagents:
Benzoic acid
Ferric Chloride
Diacetyl monoxime
orthophosphoric acid
Thiosemicarbazide
Tricholoroacetic acid
Urea - Specimen:
Serum, heparinized plasma or fluoride plasma.
Preparation of Regaents
- Reagent 1: Trichloroacetic acid, 50g/l (5%) solution
Trichloroacetic acid = 10g
Distilled water = upto 200ml - Reagent 2: Diacetyl monoxime (2,3-butanedione monoxime) solution
Diacetyl Monoxime = 2g
Distilled water = upto 500ml - Reagent 3: Acid reagent
Concentrated sulfuric acid = 44ml
Orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4), 85% = 66ml
Cadmium sulfate = 1.6 g
Thiosemicarbazide = 50mg
Distilled water = upto 500ml - Reagent 4: Colour reagent
Acid reagent (Reagent 3) = 50ml
Diacetyl monoxime reagent = 50ml - Reagent 5: Benzoic acid solution 1 g/l
Benzoic acid = 1 g
Distilled Water = 1000ml. - Reagent 6: Urea stock reference solution, 125mmol/l
Urea = 750mg
Benzoic acid, 1 g/l (0.1%) solution = upto 100ml - Reagent 7: Urea working reference solution, 10mmol/l
Urea stock reference solution = 8ml
Benzoic acid (C7H6O2), 1 g/l (0.1%) solution = upto 100ml
Preparation of Sample
To obtain protein free filtrate, take 50 ul of whole blood/serum/plasma in a centrifuge tube. Add 1 ml of TCA solution and mix. Centrifuge at high speed (3000 g) for 5 minutes to sediment the precipitated proteins and obtain a clear supenatent fluid. Do same for standard/control sample.
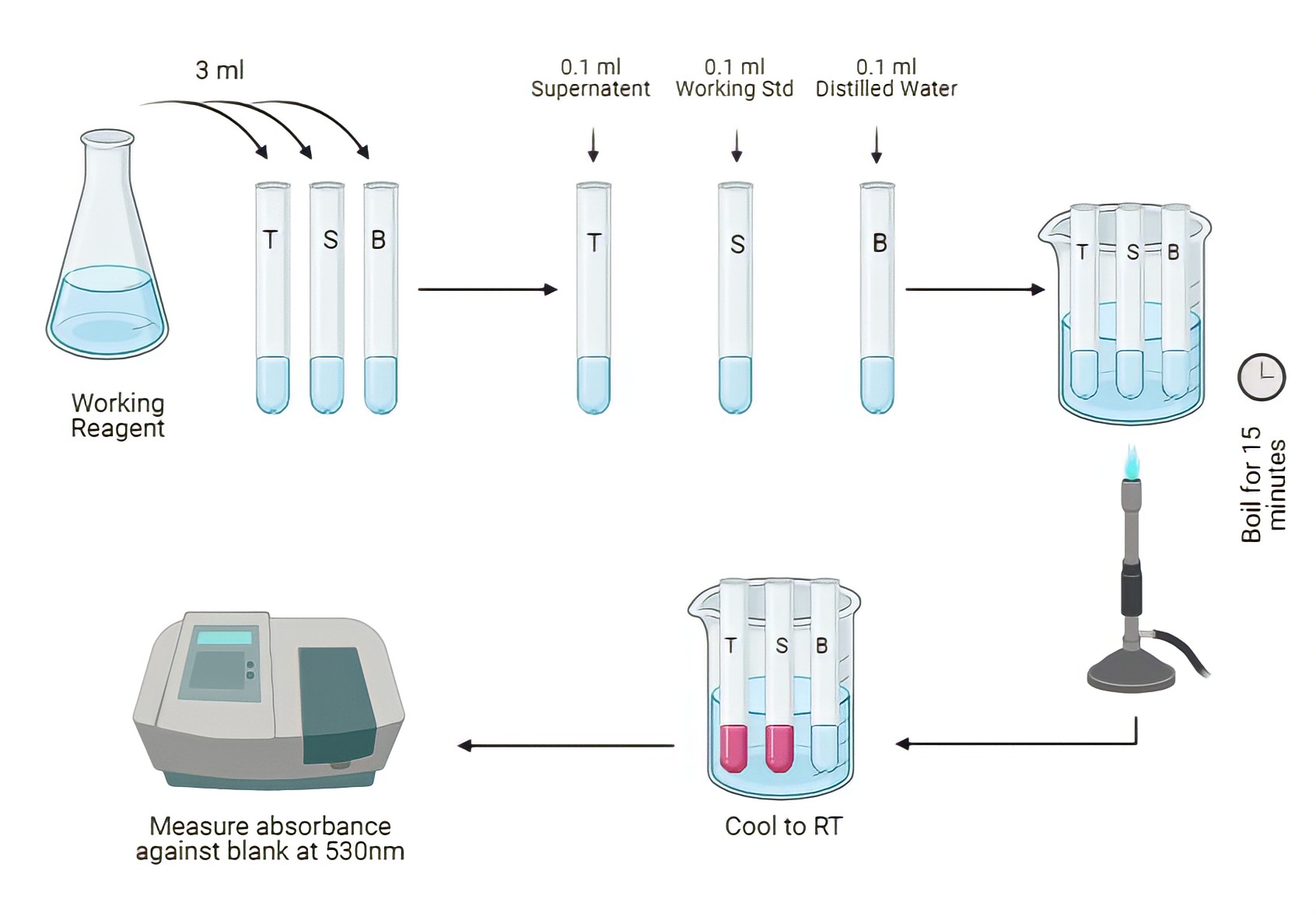
Procedure
- Take three (or more if needed) large test-tubes and label as follows:
Blank tube (B)
Standard tube (S)
Test tube (T) - Pipette into each tube as follows:
Test Standard Blank Color Reagent (Reagent 4) 3 ml 3 ml 3 ml Protein Free Filtrate 0.1 ml – – Urea Standard 10 mmol/l – 0.1 ml – Distilled water – – 0.1 ml - Mix the contents of each tube. Place all the tubes in the water-bath at 100°C for exactly 15 minutes to allow the red color to develop.
- Remove the tubes and allow them to cool in a beaker of cold water for 5 minutes.
- Measure the colour produced in a colorimeter at a wavelength of 530nm.
Calculations
Calculate the concentration of urea in the blood specimen using the following formula:
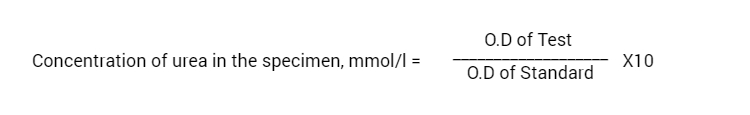
References
- World Health Organization, 2003. Manual of basic techniques for a health laboratory. World Health Organization.
- World Health Organization, 1986. Methods recommended for essential clinical chemical and haematological tests for intermediate hospital laboratories/Working Group on Assessment of Clinical Technologies. In Methods recommended for essential clinical chemical and haematological tests for intermediate hospital laboratories/Working Group on Assessment of Clinical Technologies.
- Godkar, P.B. and Godkar, D.P., 2003. Textbook of medical laboratory technology. Bhalani.
- Mukherjee, K.L., 2013. Medical Laboratory Technology Volume 3 (Vol. 3). Tata McGraw-Hill Education.

Be the first to comment