Different methods based on different properties of glucose are described for blood glucose estimation. They are:
1. Reduction Methods:
- Ferric reduction methods
- Hagedorn-Jensen ferric reduction method
- Hoffman’s method
- Cupric reduction methods
- Somogyi-Nelsen method
- Neocuproine method
- Shaffer-Hartmann method
- Folin-Wu method
- Benedict’s method
2. Aromatic amine condensation methods:
3. Enzymatic Methods:
- Glucose-oxidase Peroxidase (GOD POD) method (Trinder method)
- Hexokinase method
- Glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) method
- Kinetic method
- Polarographic method
4. Electrochemical methods:
- Glucometer
GOD-POD Method for Glucose Estimation
Being more specific, easier, and more accurate, enzymatic methods are preferred these days. Among them, the GOD-POD method is the most common method of glucose estimation.
Principle:
In the presence of atmospheric oxygen, glucose present in the specimen is oxidized by the enzyme glucose oxidase (GOD) to gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
Thus formed H2O2 oxidatively couples with 4-aminoantipyrine and phenol in presence of peroxidase (POD) to form red-colored quinoneimine dye, which is measured colorimetrically at 540nm. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the concentration of glucose present in the specimen.
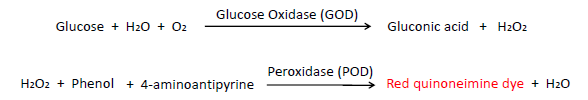
Requirements:
Specimen:
Serum, or plasma free of hemolysis. Sodium fluoride is preferred as an anticoagulant due to its antiglycolytic activity.
Reagents:
- Glucose standard (100 mg/dl)
- GOD-POD reagent: Enzyme reagent mixture containing glucose oxidase (GOD), peroxidase (POD), 4-aminoantipyrine, phenol, and phosphate buffer (pH≈7.0), some stabilizers and activators.
Instruments:
- Test tubes
- Pipettes, disposable tips, rack
- Water bath
- Colorimeter
Procedure:
- Label three clean, dry test tubes as Blank (B), Standard (S), and Test (T).
- Pipette as follows:
- Mix well and incubate at 370C for 10 minutes. Or, at room temperature (250C) for 30 minutes.
- Measure the absorbance of the standard and test sample at 540nm (green filter) against blank within 60 minutes.
| Blank | Standard | Test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GOD-POD Reagent | 1 ml | 1 ml | 1 ml |
| Distilled water | 10 µl | – | – |
| Glucose standard | – | 10 µl | – |
| Sample | – | – | 10 µl |
Calculation:
Calculate the concentration of blood glucose in the specimen using the following formula:
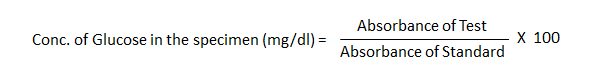
References:
- Burrin, J. M., & Price, C. P. (1985). Measurement of blood glucose. Annals of clinical biochemistry.
- Dandekar, S. P., Rane, S. A. (2004) Practical and Viva in Medical Biochemistry, New Delhi, Elsevier/Reed Elsevier. India PVT LTD.

Be the first to comment