Folin-Wu method is one of the oldest methods for the estimation of blood sugar. However, it is almost obsolete for now but is in use in countries where enzyme preparations are not easy to obtain. This method is old and not specific for glucose determination since other substances (e.g. fructose, lactose, and glutathione) also bring about a reduction. The blood glucose level when estimated by the Folin-Wu method is higher than true glucose.
Principle
Proteins from the blood are removed by 10% sodium tungstate and 2/3N sulphuric acid. The glucose present in the protein-free filtrate on boiling in an alkaline medium will be changed to enediol form. This enediol will reduce cupric ions to the precipitate of cuprous oxide. This oxide is dissolved and reacted by phosphomolybdic acid to form phosphomolybdenum blue which is blue in color. Constricted tubes (Folin-Wu tubes) are used to avoid reoxidation of cuprous oxide by atmospheric oxygen. The final blue color is measured at 680 nm which is proportional to the amount of glucose present in the specimen.
Requirements
- Folin Wu tubes
- Colorimeter
- Reagents:
- 2/3 N H2SO4: Add 2ml H2SO4 to about 50ml of D/W and dilute up to 100ml.
- 10% Sodium Tungstate: Dissolve 10 gm in 100ml of D/W.
- Alkaline Copper tartarate:
A) Dissolve 40gm sodium carbonate and 7.5 gm tartaric acid in about 400ml of D/W.
B) Dissolve 4.5 gm copper sulphate in about 100ml D/W.
Mix A and B and make volume up to 1000ml with D/W. - Phosphomolybdic acid: Dissolve 35 gm molybdic acid and 5 gm sodium tungstate in 200 ml 10% NaOH. Add it to 200ml D/W and boil for 45 minutes to remove ammonia. Cool and add slowly 125 ml of 89% phosphoric acid. Make up the volume to 500ml with D/W.
- Distilled water
- Glucose standard
Stock (1g/dl): Dissolve 1 gm of glucose in 100 ml saturated benzoic acid (0.3%).
Working standard (10mg/dl): Dilute stock 1:100 with saturated benzoic acid.
Procedure
Step 1: Preparation of protein-free filtrate:
- Add 1 ml of blood to 7 ml of distilled water and mix.
- Add 1 ml of 10% sodium tungstate.
- Add 1 ml of 2/3N H2SO4 and mix. Allow standing for 5 minutes.
- Centrifuge or filter using Whatmann number 1 filter paper.
Step 2: Testing
- Set up 3 Folin-Wu tubes as follows:
Blank Standard Test Distilled water 1 ml – – Working glucose standard – 1 ml – Protein-free filtrate – – 1 ml Alkaline copper tartarate 1 ml 1 ml 1 ml - Place the tubes in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes.
- Cool and add 1ml phosphomolybdic acid reagent to each tube.
- Shake the tubes to get rid of air bubbles. Add distilled water up to 12.5 ml mark.
- Mix and read the absorbance at 680 or red filter. Set the zero using the blank.
Calculations
Calculate the concentration of glucose in the blood specimen using the following
formula:
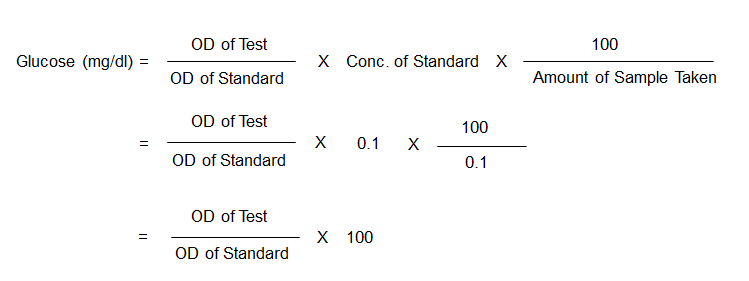
Note: 1 ml of blood was diluted 1:10 for protein precipitation. 1 ml of the diluted blood was then used for test. Therefore, the actual volume of blood used for the test is 0.1 ml.
Also, 1 ml of the working standard (10 mg/dl) contains 0.1 mg of glucose.
References
- Kolhatkar, A., Ochei, J., & McGraw, T. (2008). Medical Laboratory Science: Theory and Practice.
- Naigaonkar, A.V., (2007). A Manual Of Medical Laboratory Technology.
- Geetha, D. K. (2011). Practical Biochemistry. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd, UK.

Be the first to comment