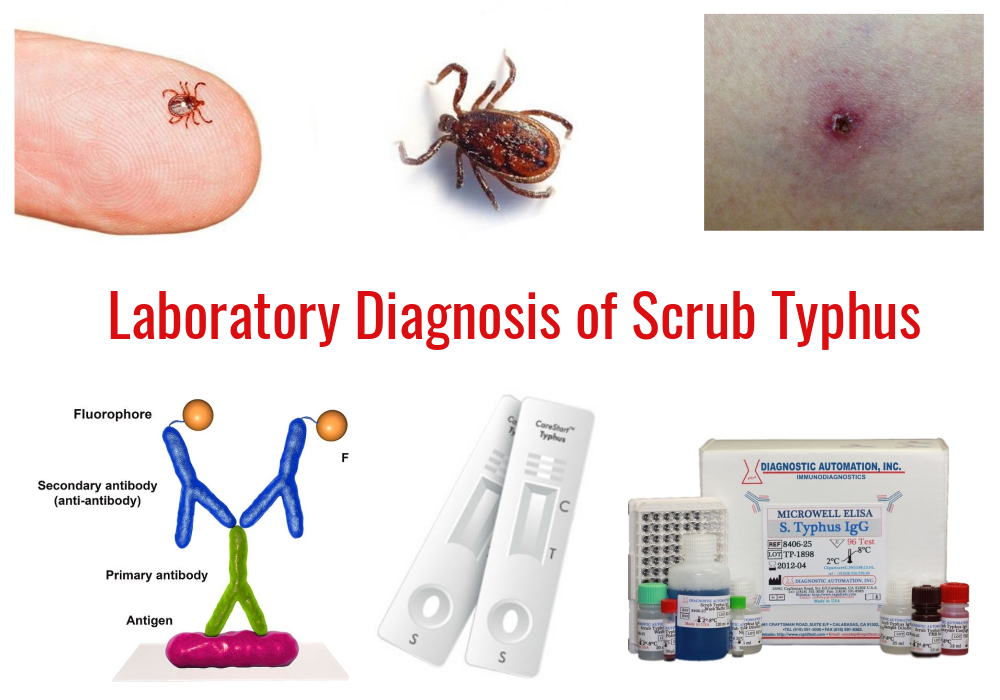
Scrub typhus is an acute, febrile, infectious disease that is caused by bacteria called Orientia tsutsugamushi. It is a zoonotic disease (an animal disease that can spread to humans) primarily affecting rodents, rabbits and marsupials. Scrub typhus is transmitted through the bite of infected chiggers (larval mites) belonging to the genus Leptotrombidium (particularly L. deliense). There is no human to human transmission.
Symptoms usually begin within 10 days of being bitten. The most common symptoms of scrub typhus include fever, headache, body aches, lymphadenopathy and sometimes maculopapular rashes and an escher at the site of bite.
The most common signs are similar to a variety of other infectious diseases like typhoid fever, malaria, leptospirosis and dengue fever etc. Thus Laboratory-based methods are more reliable and precise in the diagnosis of scrub typhus. Scrub typhus can be diagnosed in the laboratory by one of the following methods:
Direct Detection
Detection in tissue
When stained with Giemsa, Macchiavello or Gimenez stains, aggregations of bacterial particles can be detected under light microscope.
Skin biopsies from the center of petechial lesion can be examined by immunofluorescence, immune-enzyme methods and histochemical methods.
PCR Based Detection
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) based detection methods utilize genetic markers such as 56 kDa tsa, GroEL, 16s RNA and 47 kDa HtrA to detect specifically the target organism in the specimens like skin biopsy, necrotic tissue and blood mononuclear cells.
Culture and Isolation
It is expensive and laborious procedure. Orientia tsutsugamushi can’t be cultured in artificial media. It can be isolated and cultivated by inoculating in the peritoneum of mice & guinea pigs, in the yolk sac of embryonated chicken egg and in cell culture. This should be performed under BSL-3 facilities.
Serological Tests
1. Weil Felix Reaction
It is a heterophile agglutination test in which orientia antibodies are detected using antigens of certain non-motile Proteus strains. The basis of the test is sharing of an alkali stable lipopolysaccharide (LPS) antigen by some orientia/rickettsiae and by certain strains of Proteus (P. vulgaris OX19 and OX2 & P. mirabilis OX K). OX K agglutinin is found only in scrub typhus.
Weil Felix test is done as macroscopic agglutination. Serum dilutions of 1:10 to 1:640 are made to which equal amounts of antigens are added. The tubes are incubated in a water bath at 37 degree Celsius for 2 hours followed by incubation at 4 degree Celsius overnight. Complete agglutination is shown by complete clearing of the supernatant fluid and the formation of smaller masses in the bottom of the tube.
| Disease/Agglutination Pattern With: | OX19 | OX2 | OX K |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scrub Typhus | – | – | +++ |
2. Rapid lateral-flow Assays
Most of the commercially available rapid test kits for scrub typhus diagnosis are based on both IgM and IgG detection. These usually use single strip (IgG, IgM), where the Kp r56 protein is conjugated to gold particles as the indicator system.
3. Indirect Fluorescence Assay (IFA)
IFA has been considered as the gold standard and most commonly used test for serologic detection of scrub typhus due to its higher sensitivity and specificity. Karp, Kato and Gilliam’s are the most frequently used antigens.
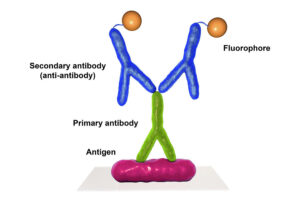
Known antigen is immobilized on a glass slide. Test serum is added over the smear. If specific antibodies are present in the serum, the antigen-antibody complex is formed. The serum is washed off and a secondary antihuman immunoglobulin conjugated to a fluorochrome is added. Upon examination under fluorescence microscope, bacteria will only be visible if they have been bound by the antibodies from the patient’s serum.
4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The 56-kDa protein (located on the outer membrane of O. tsutsugamushi) is highly reactive with patient sera and therefore preferred for use in the diagnosis of scrub typhus.
5. Other Tests
Indirect immunoperoxidase, a modification of the standard IFA method, can be used with a light microscope. Latex agglutination tests are also available.

Be the first to comment