Principle
S. aureus produces two types of coagulases: bound and free. Slide coagulase test is done to detect bound coagulase, whereas tube coagulase test is done to detect free coagulase. Both tests utilize rabbit plasma treated with anticoagulant to interrupt the normal clotting mechanism.
Bound Coagulase
It is also known as clumping factor. It is attached to bacterial cell wall and reacts directly with fibrinogen. This is shown by formation of visible mass. it doesn’t require coagulase reacting factor (CRF).
Free Coagulase
It is an extracellular enzyme (released from the cell). It converts fibrinogen to fibrin by activity of coagulase reacting factor (CRF) in plasma. This is detected by appearance of fibrin clot in the tube coagulase test. It is usaually recommended to do tube coagulase test on all ‘slide-coagulase-negative’ staphylococci.
Procedure
Slide Test
- Place two separate drops of saline on a slide.
- Using a sterile inoculating loop, emulsify one or two colonies of organism in one drop to make thick suspension of bacteria.
- Add a loopful of plasma to both the suspension and saline drop and mix gently.
- Look for immediate coarse clumping of the mixture within 10-15 seconds.
Tube Test
- Dilute the plasma 1:10 with saline.
- Take 2 test tubes and add 0.5 ml of diluted plasma to each.
- Inoculate a tube with bacterial colonies to make a cloudy suspension. Alternatively, add about 5 drops of thick 18-24 hours broth cultures.
- Incubate both tubes at 35 degree celcius for 1 to 4 hours in water bath.
- Afterward, examine both tubes for presence or absence of clots.
Results and Interpretation
Slide Coagulase Test: The formation of clumps within 10-15 seconds is positive test result. Saline and plasma mixture should show no clumping.
Tube Coagulase Test: A positive coagulase test is represented by any degree of clotting, from a loose clot suspended in plasma to a solid clot. If negative, the plasma remains a liquid.
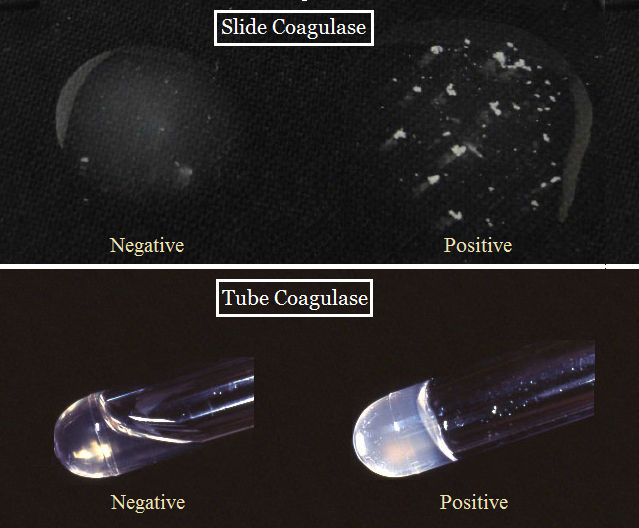
Positive coagulase test:
- Only slide coagulase positive: S.lugdunensis
- Only tube coagulase positive: S. intermedius, S. hyicus, S. schleferi subspecies coagulans
- Both slide and tube coagulase positive: S. aureus, S. delphini and some strains of S. schleferi subspecies schleferi
Negative coagulase test: Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. saprophyticus, S. warneri, S. hominis, S. caprae etc.

Be the first to comment