Wright’s stain is named for James Homer Wright, who devised the stain in 1902 based on a modification of Romanowsky stain. The stain distinguishes easily between the blood cells and hence became widely used for performing differential WBC counts and evaluate the morphology of blood cells.
Principle
Wright’s stain is a polychromatic stain consisting of a mixture of Eosin and Methylene blue. As the Wright stain is methanol based, it doesn’t require a fixation step prior to staining. However, fixation helps to reduce water artefact that can occur on humid days or with aged stain.
Methanol fixes the cells to the slide. Eosin Y is an acidic anionic dye and methylene blue is basic cationic dye. When diluted in buffered water, ionization occurs. Eosin stains the basic components such as hemoglobin and eosinophilic granules an orange to pink color. Methylene blue stains acidic cellular components such as nucleic acid and basophilic granules in varying shades of blue. The neutral components of the cells are stained by both components of the dye, producing variable colors.
Reagents
The dye may be purchased as a powder which is then mixed to methanol or a ready-made solution may be obtained.
- Staining Solution
Wright’s stain powder = 1.0 gm
Water free methanol = 400 ml - Phosphate buffer (0.15M, ph 6.5/6.8)
Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, anhydrous = 0.663 gm
Disodium hydrogen phosphate, anhydrous = 0.256 gm
Distilled water = 100 ml
Procedure
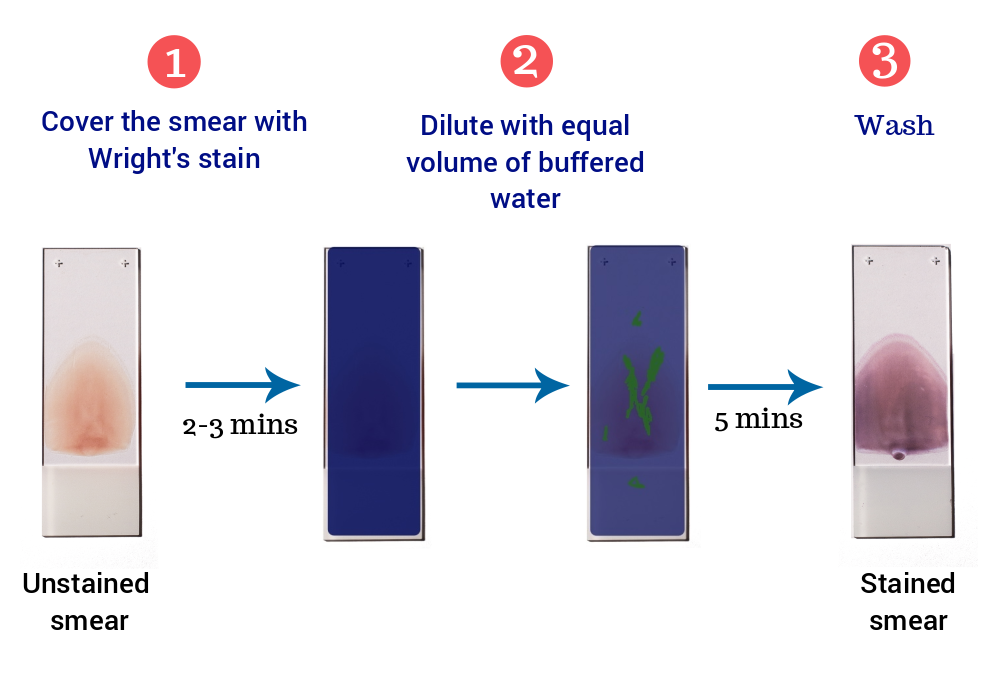
- Prepare a film of blood or bone marrow on a microscopic slide and allow to air dry.
- Place the air-dried smear on the slide staining rack, smear side facing upwards.
- Cover the blood film with undiluted staining solution. The undiluted stain fixes and partially stains the smear.
- Let stand for 2-3 minutes.
- Add approximately equal amount of buffered water (pH 6.5). The diluted stain shouldn’t overflow. Mix by gentle blowing. A metallic sheen (or green ‘scum’) should appear on the slide if mixing is appropriate.
- Leave for 5 minutes.
- Without disturbing the slide, flood the distilled water and wash until the thinner parts of the film are pinkish red.
- Allow the slide to dry at room temperature and examine under microscope.
Results
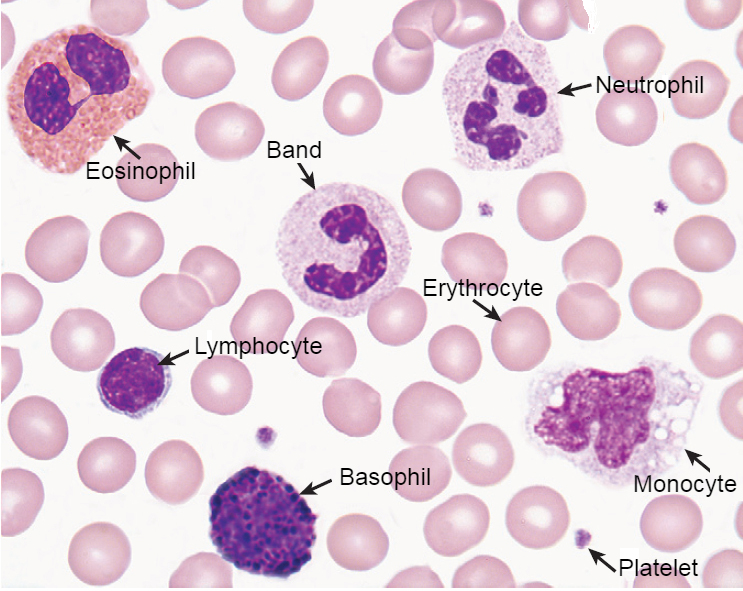
| Cells | Result |
|---|---|
| Erythrocytes | Yellowish-red |
| Neutrophils | Nucleus: Dark purple Granules: Reddish ileac granules Cytoplasm: Pale pink |
| Eosinophils | Nucleus: Blue Granules: Red to orange red Cytoplasm: Blue |
| Basophils | Nucleus: Purple to dark blue Granules: Dark purple |
| Lymphocytes | Nucleus: Dark purple Cytoplasm: Sky blue |
| Monocytes | Nucleus: Dark purple Cytoplasm: Mosaic pink and blue |
| Platelets | violet to purple granules |

Very fantastic lacturer for Wright stain
Very useful
Thanks for the process of learning laborotory subject’s
Awesome… Easy to understand