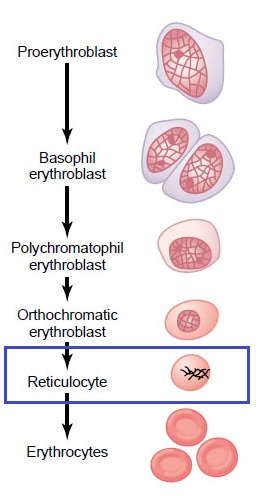
 Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs) with considerable quantities of ribosomal and mitochondrial RNA. Normally, there are a small number of reticulocytes in the peripheral blood which remain for 24-48 hours during maturation.
Reticulocytes are immature red blood cells (RBCs) with considerable quantities of ribosomal and mitochondrial RNA. Normally, there are a small number of reticulocytes in the peripheral blood which remain for 24-48 hours during maturation.Reticulocyte count is the test for determinigg bone marrow function and evaluating erythropoietic activity. It is used to classify and moniter therapy for anemias. Reticulocyte number increases when there is an increase in erythropoietic activity.
Principle
The reticulocyte count is based on the property of ribosomal RNA to react with isotonic solution of a supravital stain such as New methylene blue or brilliant cresyl blue. Supravital stains are those which stain living material. Hence, for the detection of ribosomal RNA is reticulocytes, they should be fixed.
Blood is mixed with the stain and incubated. The RNA in the cell gets precipitated as dark blue network or reticulum. Blood smear is made and examined under microscope. As a direct count is not possible, a relative count is taken against the number of RBcs and expressed as the percentage of RBC.
Requirements
- Specimen: EDTA whole blood/capillary blood
- Reagent:
New Methylene Blue
New methylene blue = 1.0 gm
Sodium citrate = 0.6 gm
Sodium chloride = 0.7 gm
Distilled water = 100 mlOR
Brilliant Cresyl Blue
Brilliant cresyl blue = 1.0 gm
Sodium citrate = 0.6 gm
Sodium chloride = 0.7 gm
Distilled water = 100 ml
Procedure
- Take 2-3 drops of dye solution in a test tube.
- Add 2-4 drops of well-mixed blood sample and mix.
- Stopper the tube and incubate at 370C for 10-15 minutes.
- After incubation, mix well and make a thin smear of stained blood.
- When dry, examine the films without fixing or counterstain.
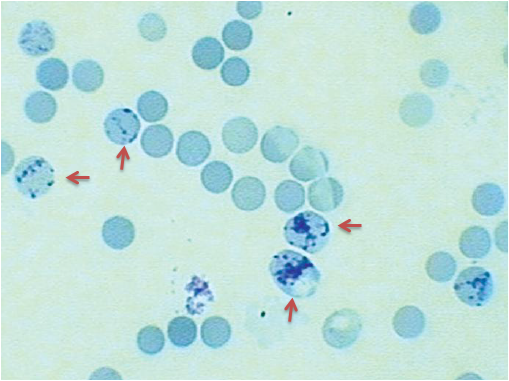
- Count 1000 RBCs and note the number of reticulocytes among them. A dark-blue reticulum or network will present in reticulocytes.
Calculation
1. Retculocyte Percentage
This is the percentage of reticulocytes per 1000 RBCs.

2. Absolute Reticulocyte Count
The absolute reticulocyte count (ARC) is the actual number of reticulocytes in 1 L of whole blood.

3. Corrected Reticulocyte Count
In specimens with a low hematocrit, the percentage of reticulocytes may be falsely elevated because whole blood contains fewer RBCs. A correction factor is used, with the average normal hematocrit considered to be 45%.
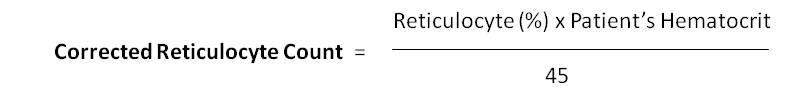
Reference Ranges
Adults: 0.2-2%
Infants: 2-6%
Childrens upto 5 years= 0.2-5.0%
Clinical Significances
| Reticulocytosis | Reticulocytopenia |
|---|---|
Condition where there is an increase in reticulocytes. Such as:
|
Condition where there is an decrease in reticulocytes. Such as:
|

I’m unfamiliar with the incubation step. 370 C? We let it sit at room temperature for 10 minutes.
This article is very helpful and easy to understand.
Hello Kate, That is 37°C. Incubation in any of two ways, room temperature or 37°C works fine. In general, incubation at room temperature for 20 minutes or 10–15 minutes at 35–37°C gives better results.
Incubation is better than room temp.procedure. Room temp. Will not be stable.
Make a more new posts please 🙂
___
Sanny
Please any new article?
hi ! could you give the reference where the total count of RBC is 1000? I just find a total count of 100.
Thank you
Thank you very for very nice and easy to understand explanation. Best of luck.