Principle
May Grunwald-Giemsa stain is a combination of two stains: May Grunwald stain and Giemsa stain.
- May Grunwald stain is alcohol-based stain composed of methylene blue and eosin.
- Giemsa stain is alcohol-based stain composed of methylene blue, eosin and azure B.
The working principle of MGG stain is the same as that of other Romanowksy stains. Polychromatic Romanowksy dyes contain different ratios of methylene blue (and the reagent-related thiazine dyes, such as azure B), as the cation (+vely charged, basic) component, and eosin Y as the anion (-vely charged, acidic) component. Cation and anion components in combination produce the well-known Romanowsky effect or metachromasia.
The solvent methanol initially fixes the cells. The basic dyes carry net positive charges; consequently, they stain nuclei (because of the negative charges of phosphate groups of DNA and RNA molecules), granules of basophil granulocytes, and RNA molecules of the cytoplasm. The eosin carries a net negative charge and stains red blood cells and granules of eosinophil granulocytes. Buffer solution of pH 6.5-6.8 is used to enable the dye to precipitate and bind well with the cellular material.
Reagents
May Grunwald Stain
- Stock solution:
May Grunwald dye= 0.3 gm
Methanol = 100 ml - Working Solution:
Stock solution= 20 part
Phosphate Buffer (pH 6.8)= 30 part
Giemsa Stain
- Stock Solution:
Giemsa Powder= 1 gm
Glycerine= 66ml
Absolute ethanol= 66ml
Mix giemsa and glycerine, place in 60C oven for 30 minutes 2 hr. Add 66ml methanol - Working Solution:
Stock Giemsa= 50 drops
Distilled Water=50ml
Procedure
- Prepare a thin smear and air dry.
- Fix smears for 5-10 minutes with methanol.
- Stain the smear in May Grunwald working solution for 10 minutes.
- Rinse in pH 6.8 buffer.
- Stain the slides with diluted Giemsa stain for 30 minutes.
- Wash the smears with distilled water and let them dry.
- Mount the slide with DPX and examine under microscope.
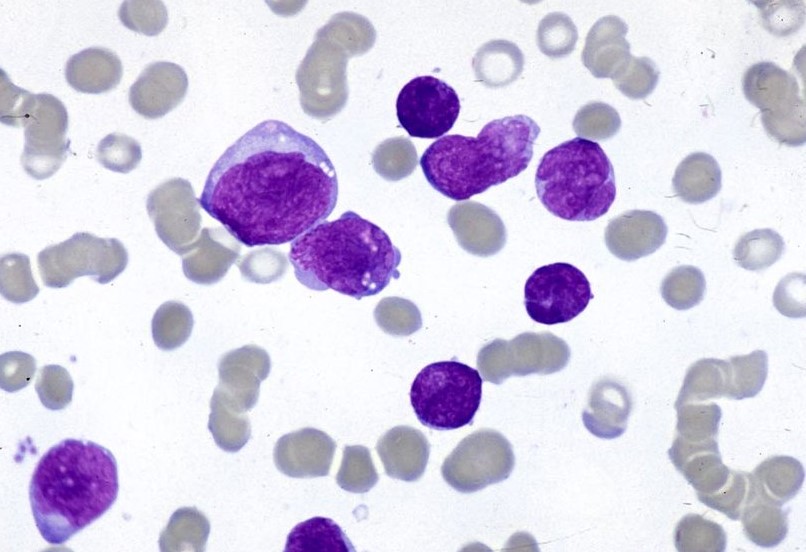
Results
- Erythrocytes: Light pink to light purple
- Platelets: Granules – Reddish purple
- Lymphocytes/monocytes: Nuclei – Dark purple, Cytoplasm – Sky blue
- Neutrophils: Nuclei – Dark blue, Granules – Reddish purple, Cytoplasm – Pale pink
- Eosinophils: Nuclei – Blue, Granules – Red/orange red, Cytoplasm – Blue
- Basophils: Nuclei – Dark blue, Granules – Purple
References
- Dey, P. (2018). Basic and advanced laboratory techniques in histopathology and cytology. Springer Singapore.
- Matutes, E., Pickl, W. F., Van’t Veer, M., Morilla, R., Swansbury, J., Strobl, H., … & Ludwig, W. D. (2011). Mixed-phenotype acute leukemia: clinical and laboratory features and outcome in 100 patients defined according to the WHO 2008 classification. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology, 117(11), 3163-3171.
- Product Information May-Grünwald Giemsa, Avantor™ Performance Materials.

Be the first to comment